
Higher patient mortality in type 2 2020 simultaneous pancreas/kidney (SPK) transplants - a preliminary registry analysis
Angelika Gruessner1, Subodh J. Saggi1, Rainer WG Gruessner1.
1Medicine, SUNY Downstate medical Center, Brooklyn, NY, United States
Introduction: Over the last decade the number of simultaneous pancreas/kidney transplants in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) increased. No difference in outcomes between patients with type 1 or type 2 DM could be found before. The COVID-19 pandemic had especially an impact on people which were older, had a high BMI and were more frequently Black with a high likelihood to have type 2 DM. This study investigates the patient survival in SPK during 2020.
Methods: 797 primary deceased donor SPK transplanted in diabetic patients between in 2020 were included. The outcome was also compared with outcome in 2019. Univariate and multivariable models were developed to identify risk factors during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results: The number of SPK transplants in in type 1 DM increased after May 2020 and remained constant. Transplants in type 2 DM declined lightly in April but recovered afterwards and also remained stable. The characteristics by diabetes type are listed in Table 1 and show the known differences in the diabetic patient population.
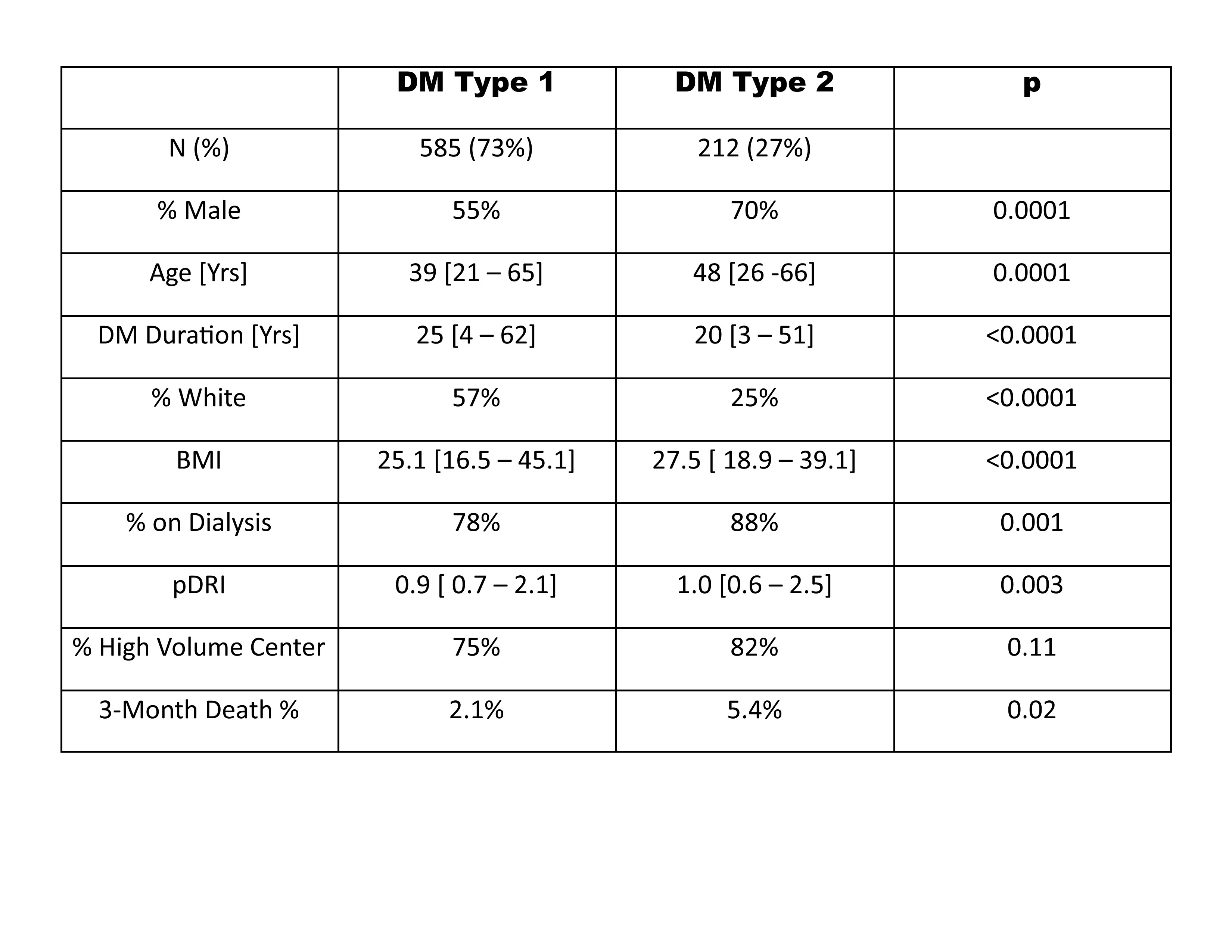
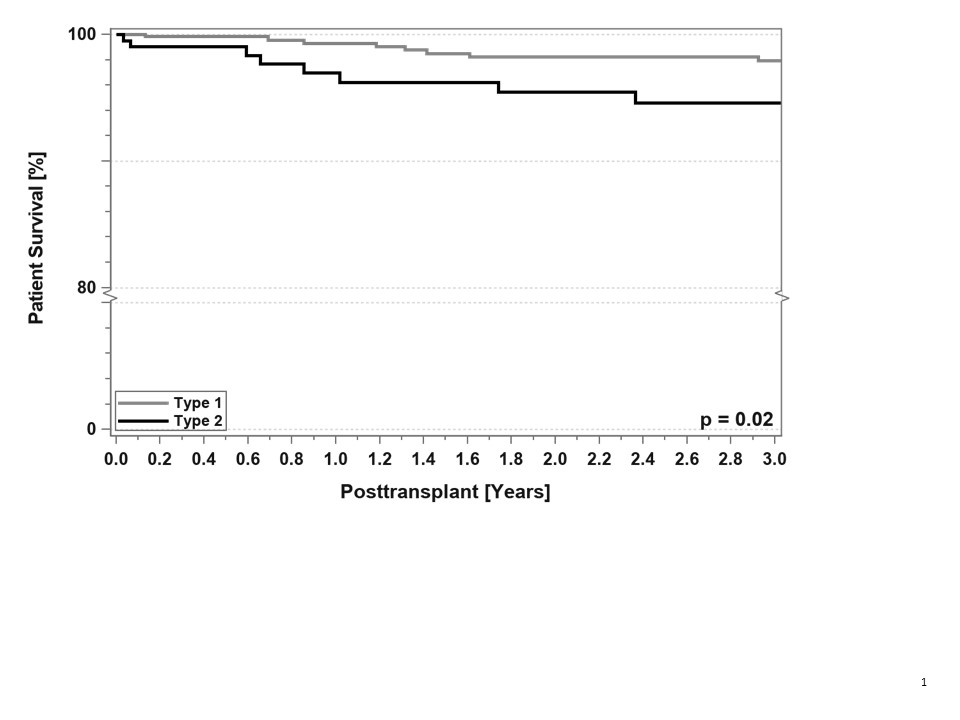
There was an overall significant difference in short-term patient survival between 2019 and 2020. In 2019 overall patient death at 3 months was 0.9% compared to 3% in 2020 (p<0.0001). There was no difference in 3 months patient survival between the diabetes types in 2019 (p=0.50) but a significant difference could be found in 2020 (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Most of the causes of death were reported vague as cardio-vascular or cardio-pulmonary arrest. A multivariable analysis of the influential risk factors for patient death in 2020 transplants identified type 2 compared to type 1 DM with an increased relative risk of 2.4 [1.1 – 5.9] and a BMI over 30kg/m2 with a relative risk increase of 2.5 [1.07-5.8]. Other factors did not show a significant impact.
Conclusion: This preliminary studied showed the increased risk factors for a COVID-19 infection also in the deaths of early SPK transplants.